Where the soul of the forest whispers in the mist
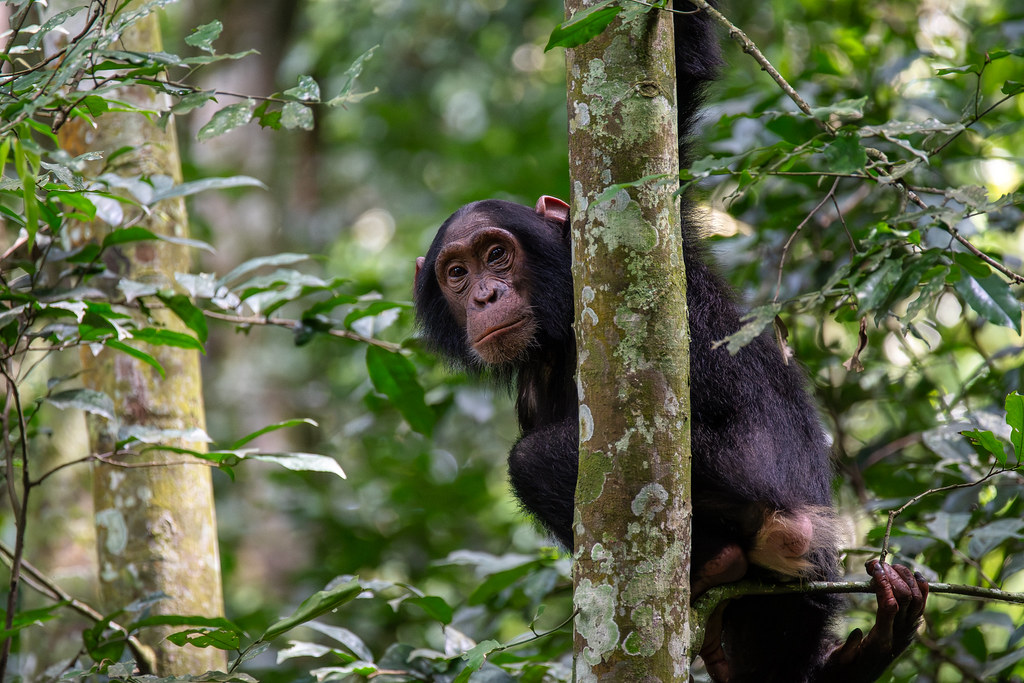
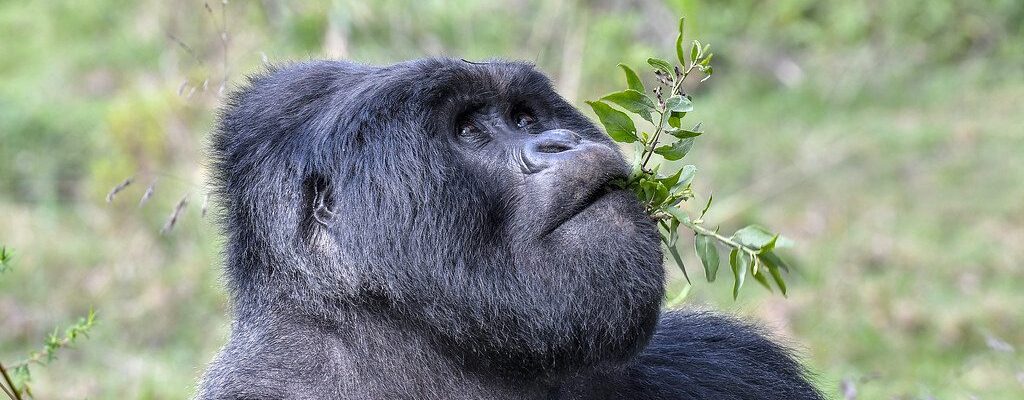
Chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes) are among Africa’s most intelligent and socially complex primates. Native to tropical forests, savannah-forest mosaics, and woodland regions across central and western Africa, they are closely related to humans, sharing approximately 98–99% of our DNA. This genetic proximity is reflected in their advanced cognitive abilities, intricate social behaviors, and tool-use practices.
Chimpanzees play a vital role in forest ecosystems as seed dispersers, hunters, and indicators of environmental health. They are highly adaptable yet vulnerable, with populations declining due to habitat loss, poaching, disease, and human encroachment. Conservation efforts across Africa aim to protect their habitats, mitigate human-wildlife conflict, and ensure the survival of these remarkable primates.
So lace up your boots, grab your camera, and prepare to meet the wild — this is where your gorilla trekking dreams and unforgettable safari adventures truly begin.
Truly Iconic Highlights in Uganda
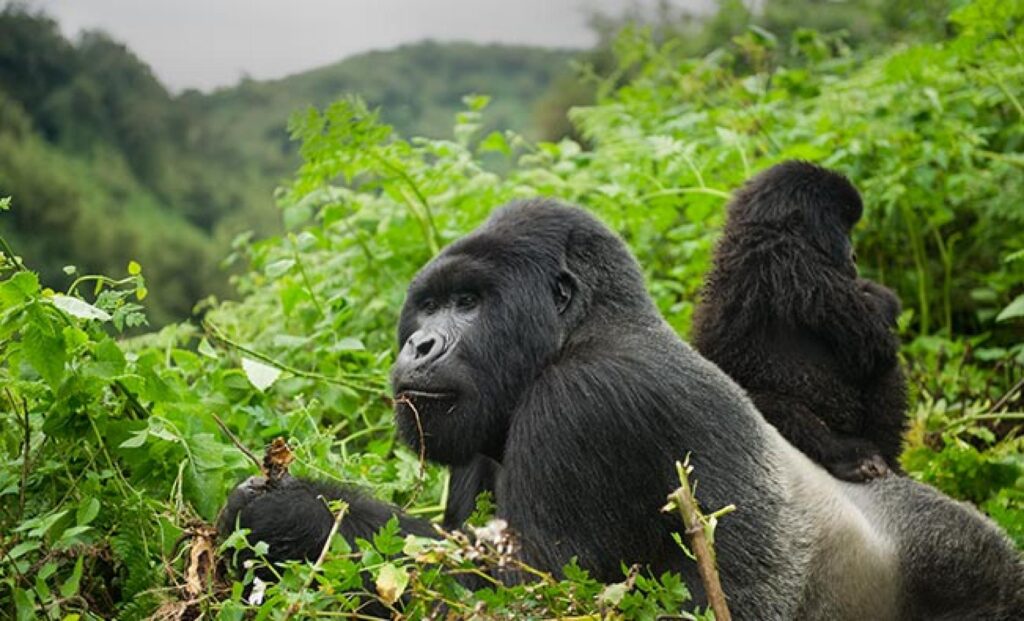
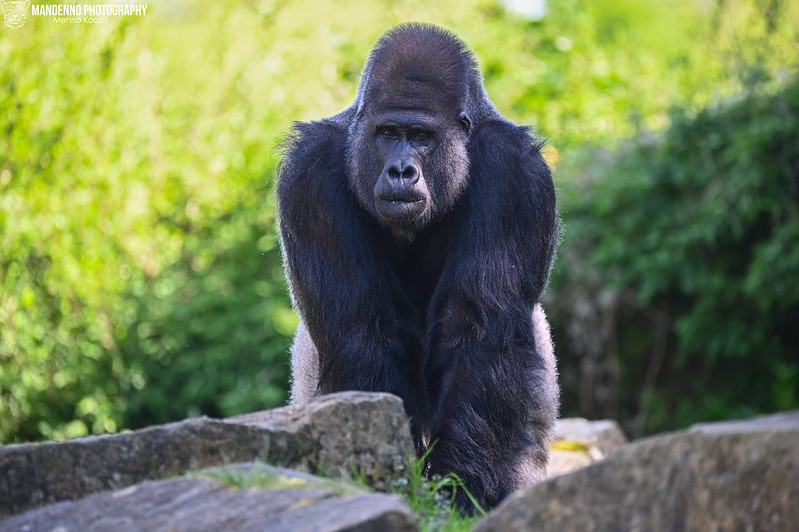
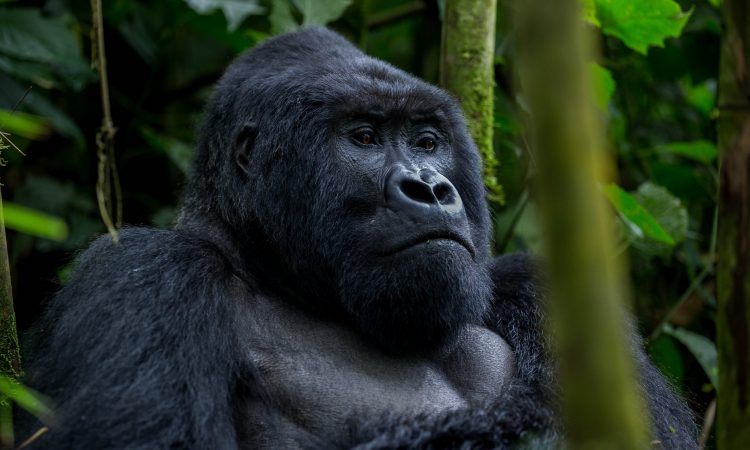
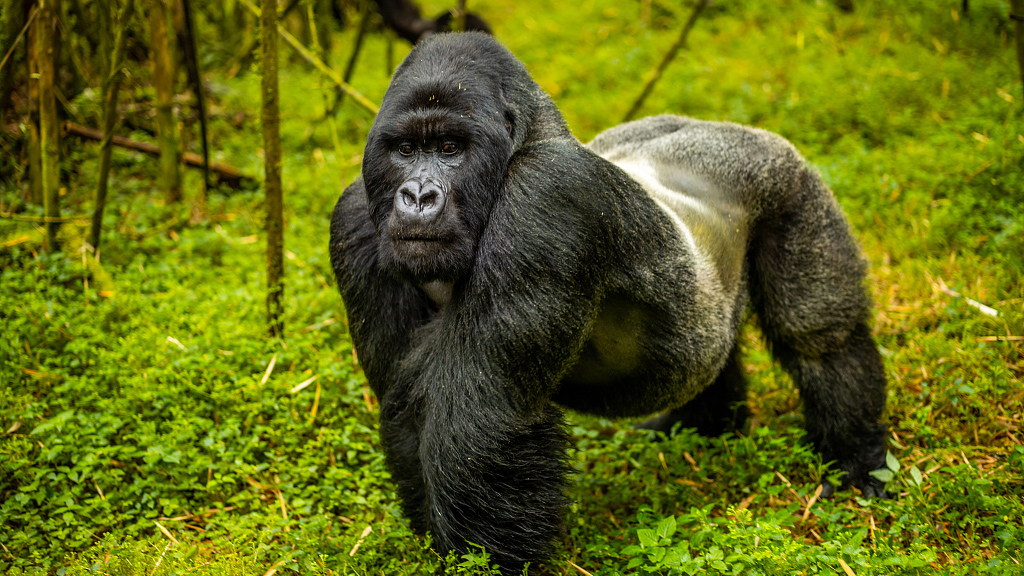
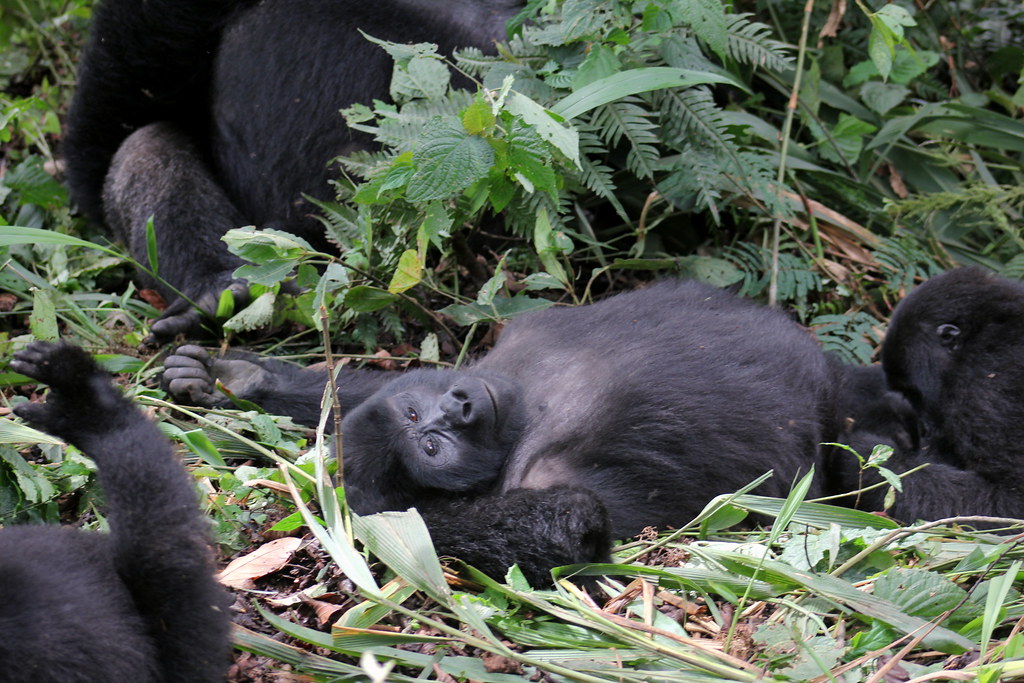
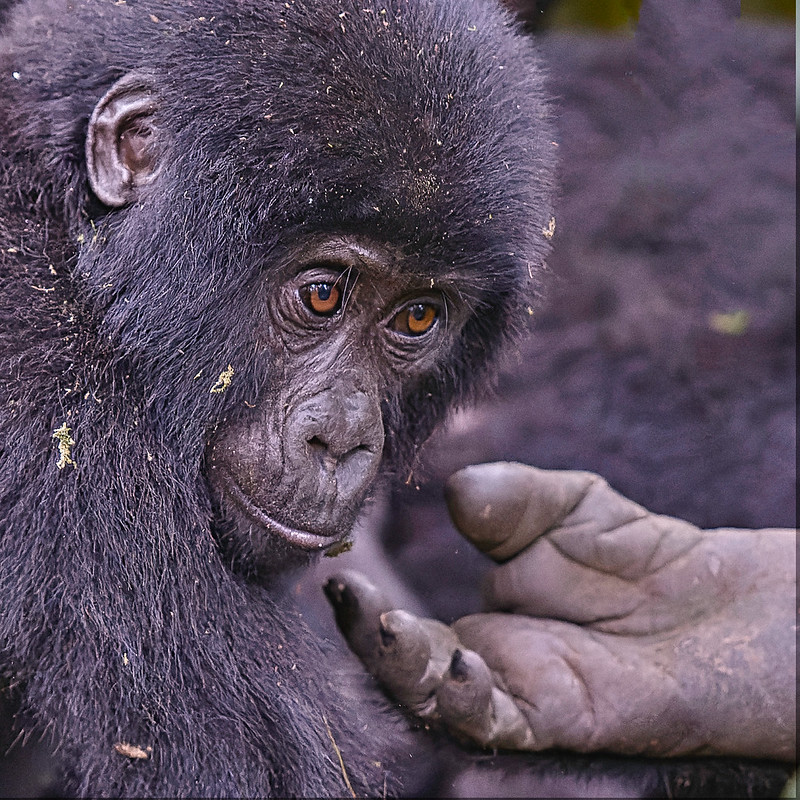
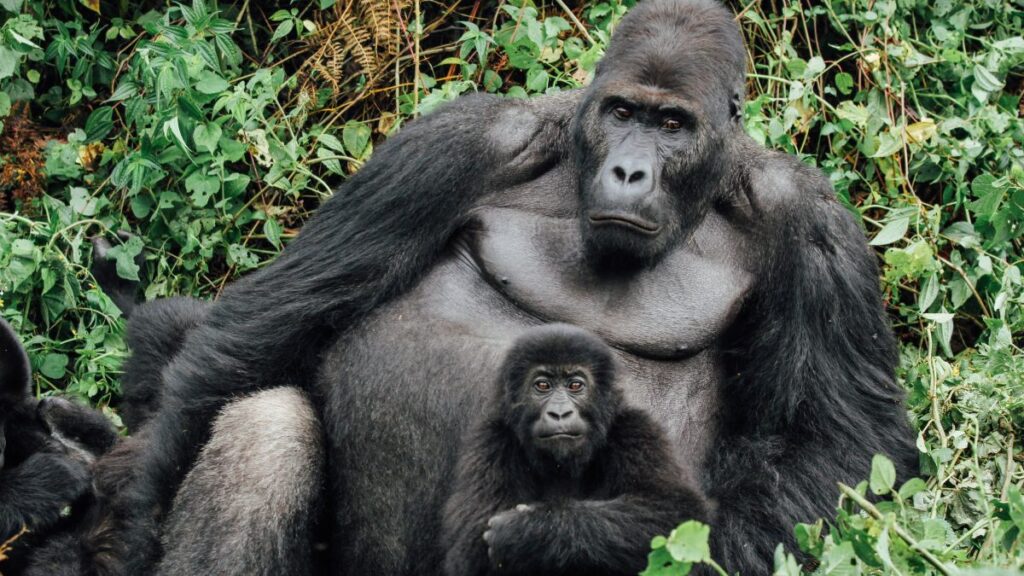
Trek through Bwindi’s mystical rainforest and meet the endangered mountain gorillas in their breathtaking natural home.
Encounter mountain gorillas and golden monkeys on Mgahinga’s misty volcanic trails, where culture and alpine wildlife thrive together.
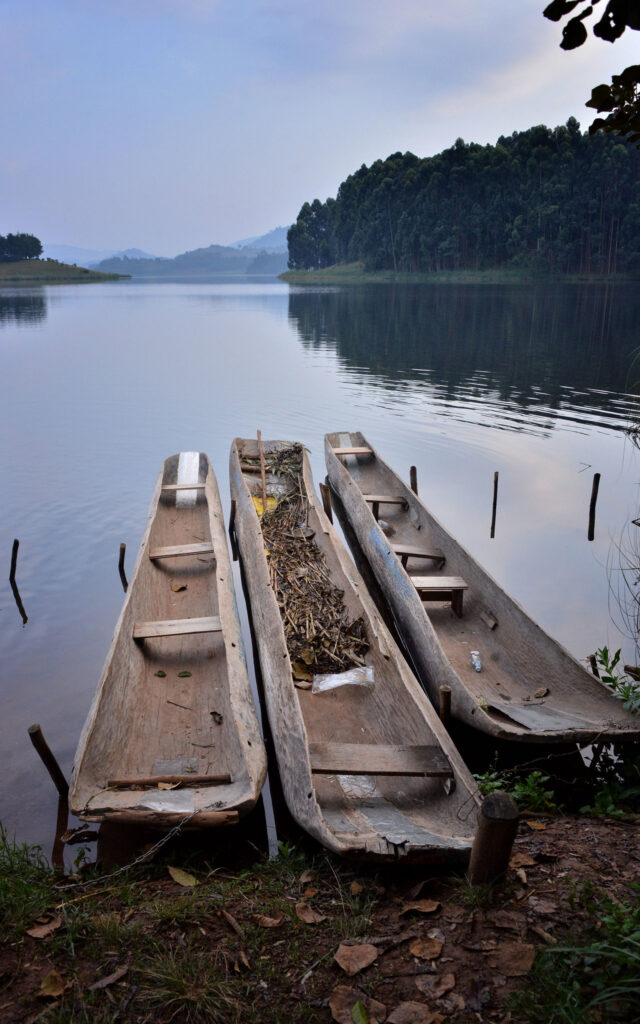
Unwind after your trek with a peaceful canoe ride across Lake Bunyonyi, Uganda’s most tranquil and scenic highland lake.
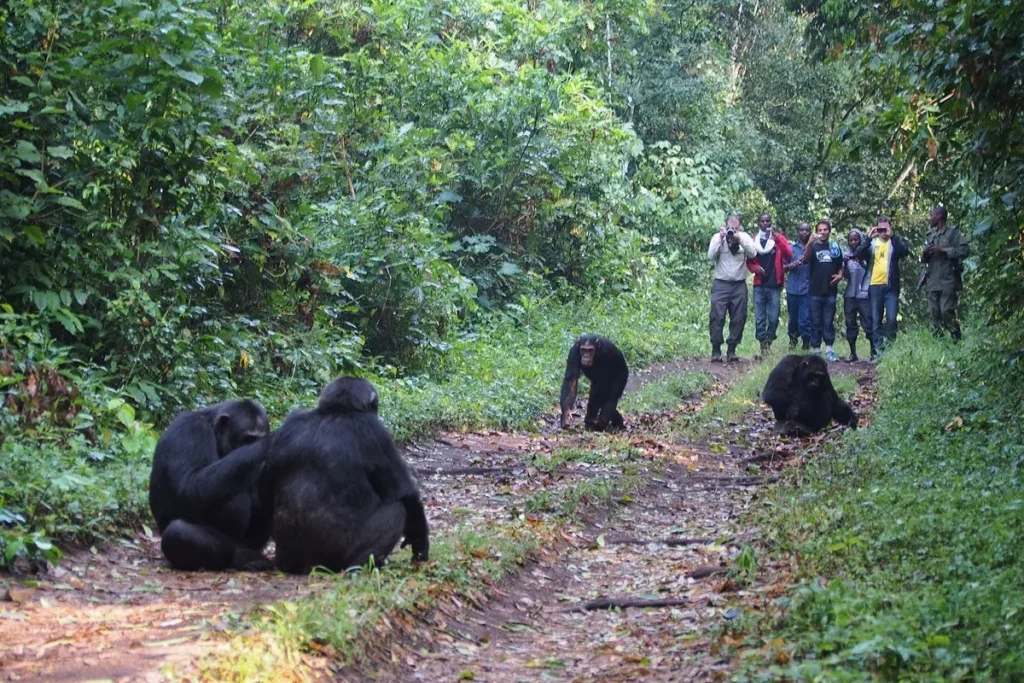
Enhance your gorilla trekking safari with an optional chimpanzee encounter in Uganda’s lush forests, adding depth and diversity to your primate adventure
Gorilla Trekking Tours in Uganda – Our Most Popular Itineraries.
Explore our gorilla trekking safaris for every traveler—solo, family, budget, or luxury. All tours include permits, transport, accommodation, meals, and park fees. Whether for a quick trip or a deeper adventure, we’ve got you covered.
Overview of Chimpanzees
Physical Characteristics and Morphology
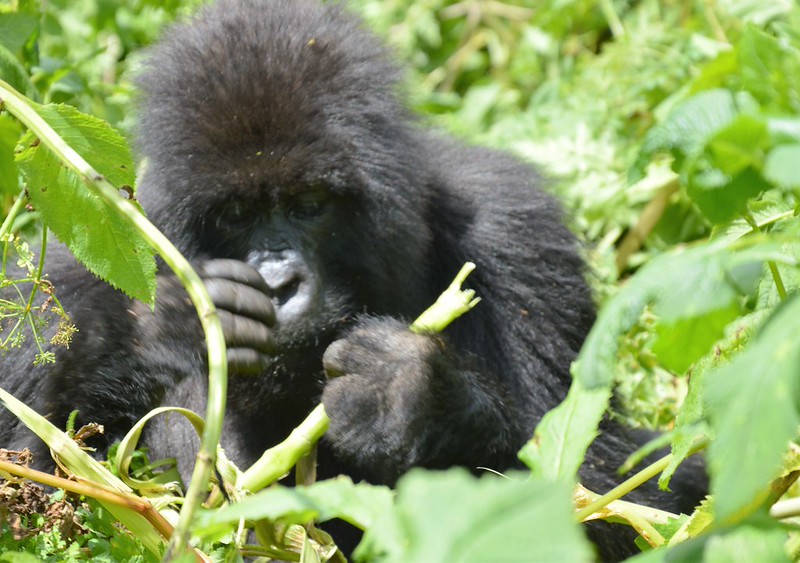
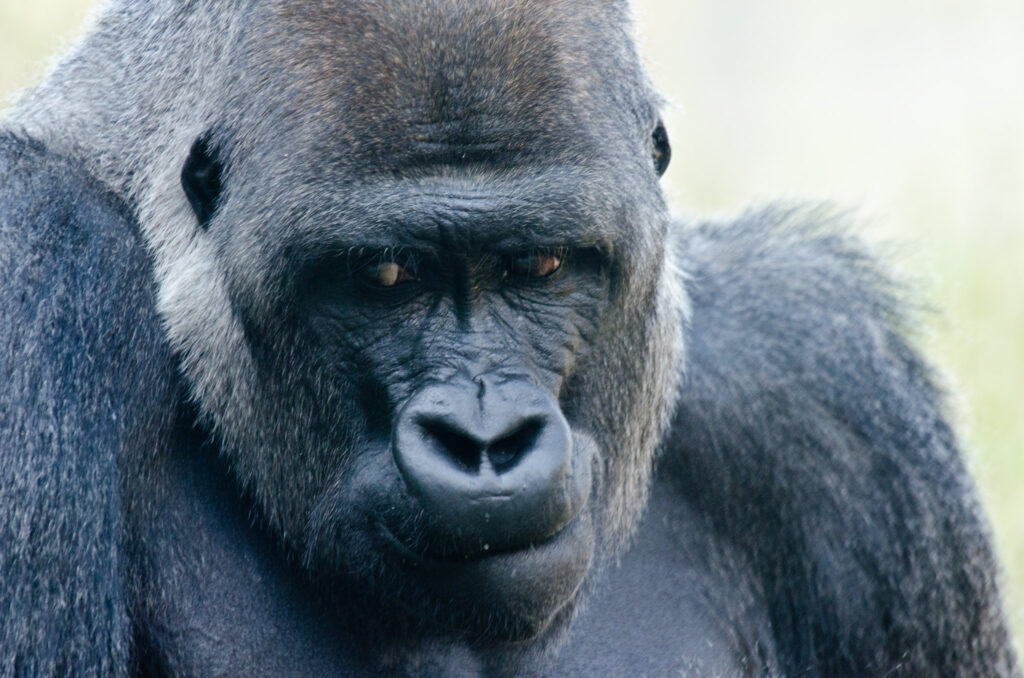
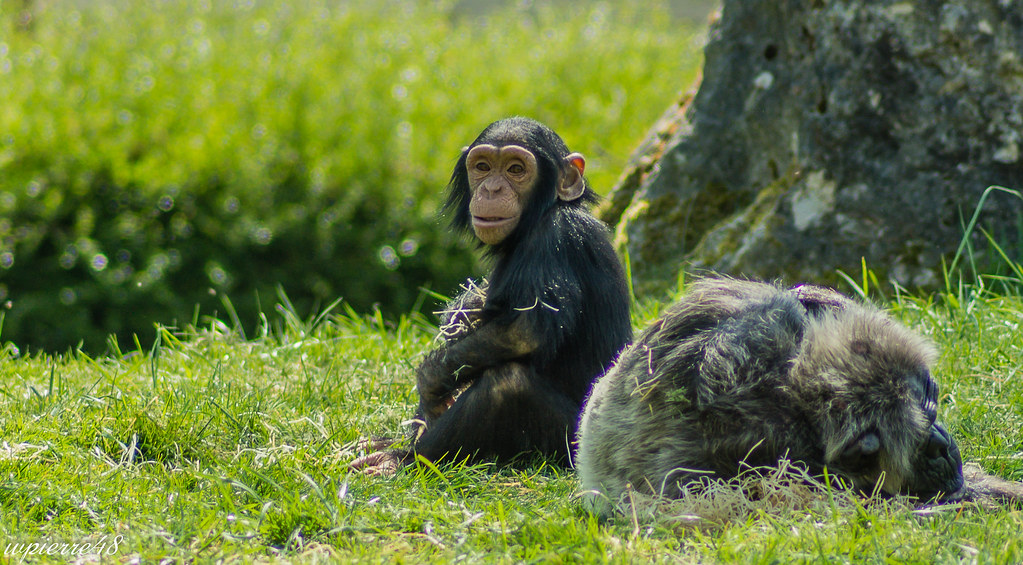
Adult chimpanzees are robust, with dark hair covering most of their bodies except for the face, ears, palms, and soles. Males generally weigh between 40–60 kilograms, while females are slightly smaller, averaging 30–50 kilograms. Adults can reach a height of 1–1.7 meters when standing upright. Their long arms and strong upper body allow them to climb trees efficiently and swing across branches, although they are also adept at walking bipedally for short distances.Chimpanzees have highly expressive faces and hands, which they use to communicate emotions, intentions, and social cues. Their opposable thumbs and advanced dexterity enable them to manipulate objects, use tools, and perform intricate tasks, highlighting their cognitive sophistication.
Geographic Distribution and Habitat
Chimpanzees are found across 21 African countries, including Uganda, Rwanda, Democratic Republic of Congo, Gabon, Cameroon, and Sierra Leone. They inhabit a variety of habitats, including tropical rainforests, dry forests, montane forests, and woodland savannahs.In Uganda, chimpanzees are most commonly observed in Budongo Forest, Kibale National Park, and Mgahinga National Park, where dense forest cover, abundant fruiting trees, and water sources provide optimal conditions. Habitat selection is influenced by food availability, predation pressure, and human disturbance, with chimpanzees preferring areas that balance safety, nutrition, and social needs.
Diet and Feeding Ecology
Chimpanzees are omnivorous with a diet dominated by fruits, leaves, seeds, nuts, and flowers. They supplement their diet with insects, small mammals, eggs, and occasionally meat, obtained through coordinated hunting of monkeys or small ungulates.Their feeding behavior is highly flexible, reflecting seasonal variations in resource availability. For instance, during fruit scarcity, chimpanzees rely more heavily on leaves, bark, and seeds. They are also known for their tool-use skills, such as termite fishing with sticks, nut-cracking with stones, and leaf-sponging to extract water, showcasing remarkable problem-solving abilities and cultural transmission of knowledge across generations.
Social Structure and Behavior
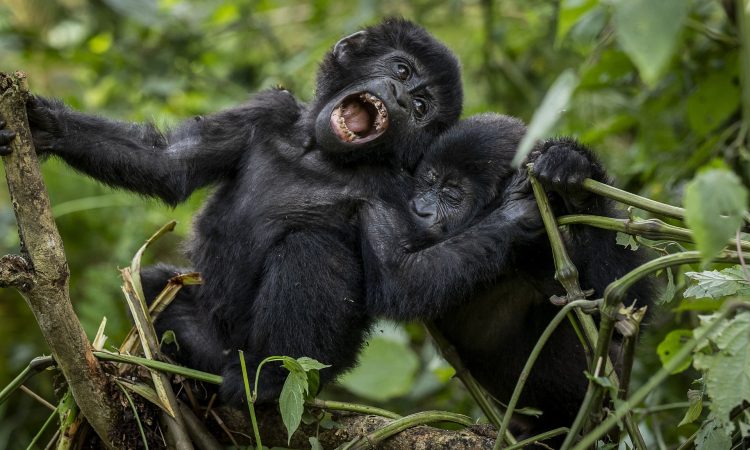
Chimpanzees live in fission-fusion societies, where group composition changes dynamically throughout the day. Communities can range from 20 to over 100 individuals, with smaller subgroups splitting off for foraging, travel, or other activities.Social hierarchies are typically male-dominated, with alpha males maintaining status through a combination of strength, alliances, and intelligence. Grooming plays a crucial role in maintaining social bonds, reducing tension, and reinforcing hierarchies. Female chimpanzees often occupy central roles in nurturing offspring, forming alliances, and facilitating social cohesion.Communication among chimpanzees is complex, incorporating vocalizations, facial expressions, gestures, and body postures. Alarm calls, food calls, and pant-hoots convey information about danger, resources, and social status, demonstrating sophisticated social awareness and emotional intelligence.
Reproduction and Life Cycle
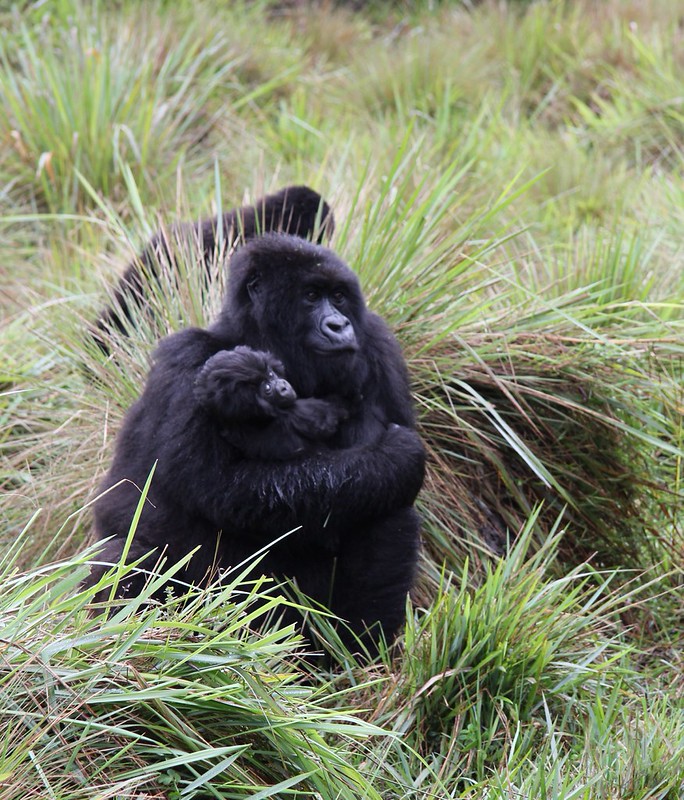
Female chimpanzees typically reach sexual maturity around 12–13 years, while males mature slightly later. Breeding occurs year-round, with females exhibiting visible sexual swellings during estrus to signal fertility. Gestation lasts approximately eight months, and usually, a single infant is born.Infants are entirely dependent on their mothers for several years, with weaning occurring around three to five years of age. Chimpanzee juveniles engage in play, learning social norms, foraging skills, and tool use through observation and imitation. Lifespan in the wild ranges from 35 to 50 years, with some individuals exceeding 60 years under favorable conditions.
Role in Ecosystems
Chimpanzees are keystone species, playing a vital role in seed dispersal and forest regeneration. By consuming fruits and excreting seeds at different locations, they facilitate plant diversity and forest structure. Their predation on insects and small mammals also contributes to ecological balance.Their presence indicates healthy, undisturbed habitats, making them important indicator species for forest ecosystem integrity. Protecting chimpanzees directly supports the broader biodiversity and functioning of African tropical forests.
Conservation Status and Threats
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) lists chimpanzees as Endangered, with population declines exceeding 50% over the last 60 years. Primary threats include habitat destruction from agriculture, logging, and mining, as well as poaching for bushmeat, live capture, and traditional medicine. Disease outbreaks, including Ebola, have also had devastating impacts on local populations.
Conservation efforts focus on habitat protection, anti-poaching measures, law enforcement, and community engagement. National parks and wildlife reserves in Uganda, Rwanda, and DRC provide critical refuge for chimpanzees, while eco-tourism initiatives, including guided chimpanzee tracking, support local economies and conservation awareness.
Chimpanzees in Tourism and Research
Chimpanzee trekking has become an important component of eco-tourism in Africa, particularly in Uganda and Rwanda. Guided tracking experiences allow visitors to observe chimpanzees in their natural environment while contributing to conservation revenue and local livelihoods.Research on chimpanzees has been equally transformative, revealing insights into tool use, problem-solving, social complexity, and emotional intelligence. Studies by primatologists such as Jane Goodall have underscored the species’ remarkable adaptability and cognitive abilities, highlighting the importance of long-term monitoring and habitat preservation.
Human-Chimpanzee Interaction and Conservation Education
Effective conservation requires minimizing conflict and fostering coexistence between humans and chimpanzees. In areas where agricultural encroachment or settlement borders forests, chimpanzees may raid crops, leading to tension with local communities. Community-based initiatives focus on education, conflict mitigation, and sustainable livelihoods to reduce these challenges.Tourism, when responsibly managed, serves as a conservation tool, providing funding for habitat protection, research, and local development. By engaging communities and educating visitors, conservation programs strengthen awareness of the species’ ecological and cultural importance.
Preserving Our Closest Relatives
Chimpanzees embody the complexity, intelligence, and adaptability of primates, reflecting traits remarkably close to humans. Their ecological role, social sophistication, and cultural behaviors underscore their importance in tropical forests and highlight the urgent need for protection.Preserving chimpanzees requires a holistic approach, combining habitat conservation, community involvement, law enforcement, and sustainable eco-tourism. Observing these magnificent primates in the wild offers not only unforgettable experiences but also a deeper understanding of our own evolutionary roots. The survival of chimpanzees is inseparable from the health of Africa’s forests, making their conservation a critical priority for biodiversity and humanity alike.
More Gorilla Trekking Information to Know.
Gorilla trekking goes far beyond just the hike — it’s a deep, emotional journey into the heart of Africa’s last wild rainforests. Knowing the right timing, permits, fitness tips, and park details can turn your experience from good to unforgettable.
In the Realm of Giants – Bwindi & Mgahinga in Frames.
Wander through an elegant gallery capturing Uganda’s most exclusive gorilla sanctuaries, where ancient forests cradle the last mountain gorillas in a world of mist, mystery, and majesty.
Essential Planning Tips for Visiting Uganda’s National Parks.
Get ready for the wild heart of Africa with expert travel tips on when to visit, what to pack, where to go, and how to make the most of your safari across Uganda’s breathtaking national parks.
Why Uganda for Gorilla Trekking?
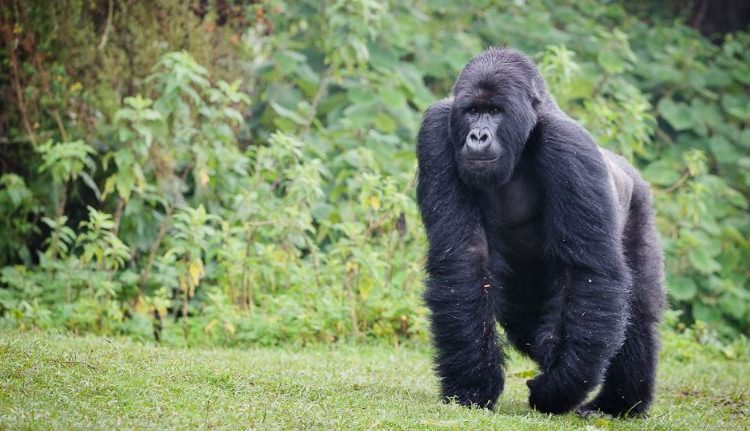
Uganda is not just a destination — it's the very soul of gorilla trekking. With over half of the world’s remaining mountain gorillas calling its misty forests home, Uganda offers the rarest encounters in their most authentic setting. Here, your journey is not rushed or crowded. Instead, you’re guided by experienced rangers through pristine jungles where gorillas live as they always have — wild, free, and magnificent
From insider travel insights to unforgettable trekking guides, our blog is your trusted path into Uganda’s wild heart — connecting you with mountain gorillas, breathtaking landscapes, and the soul-stirring adventures that make this land unlike any other.